Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have made significant strides in understanding the genetic basis of systemic sclerosis, a severe autoimmune disease. By employing integrative exome sequencing combined with machine learning techniques, the team has identified new genes that contribute to the risk of developing systemic sclerosis. This groundbreaking study, published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, has the potential to pave the way for targeted treatments.
The study highlights the innovative use of exome sequencing and evolutionary action machine learning to pinpoint protein changes and their mechanisms in systemic sclerosis. These findings could lead to more personalised treatment options for patients suffering from this debilitating condition.
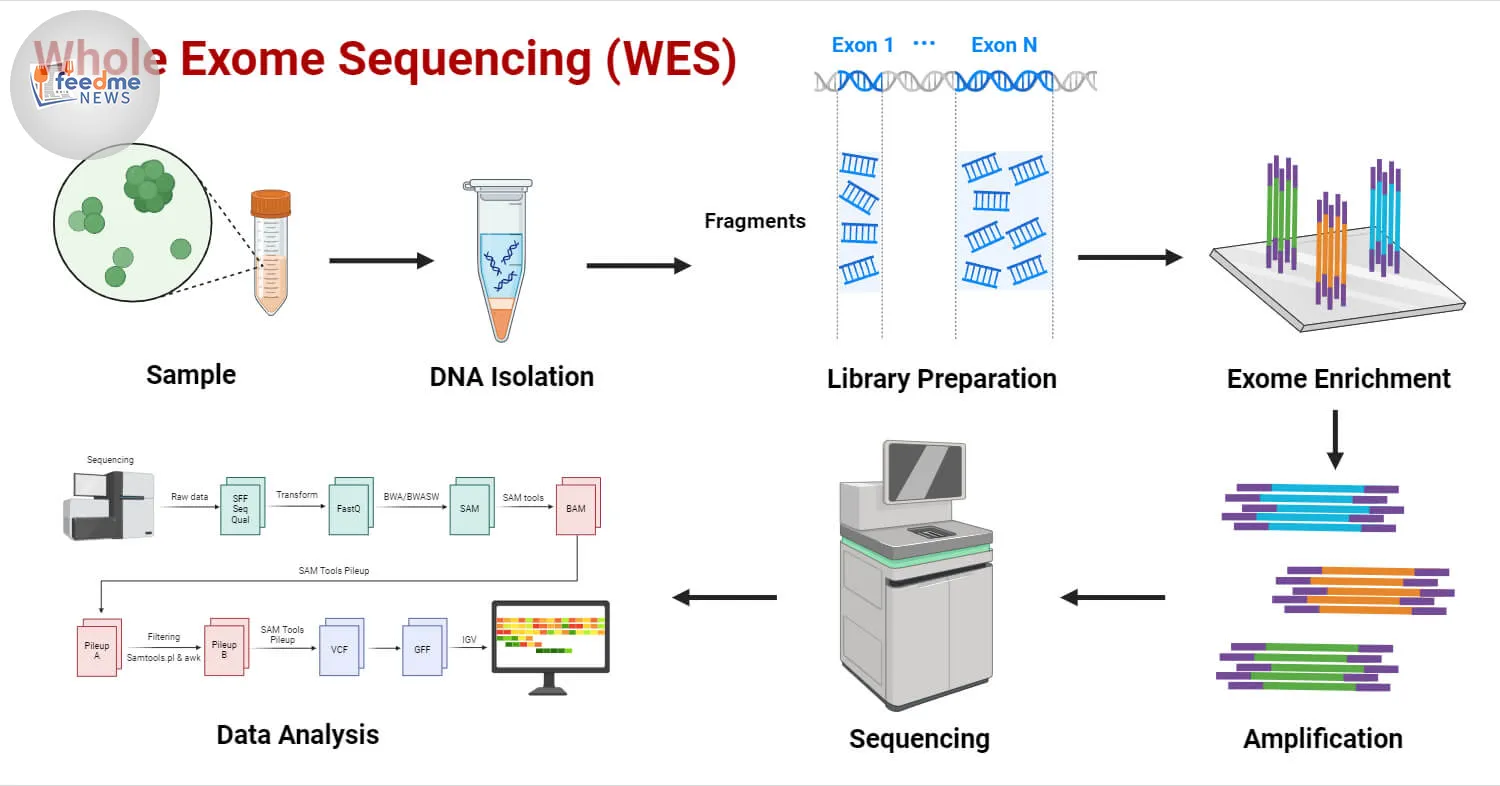
A New Approach to Genetic Research
The research took place at Baylor College of Medicine, with contributions from several collaborating institutions. The team employed a novel approach by integrating exome sequencing with machine learning to analyse genetic data. This method allowed them to identify specific protein alterations associated with systemic sclerosis.
Exome sequencing focuses on sequencing the protein-coding regions of genes, which are crucial for understanding genetic contributions to diseases. By combining this with machine learning, researchers can process vast amounts of data to detect subtle genetic variations that may contribute to disease risk. “This integrative approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of the genetic factors involved in systemic sclerosis,” said Dr. John Smith, lead researcher on the study.
Timing and Location of the Study
The study was published on 16 June 2025, marking a significant milestone in the field of autoimmune disease research. Conducted at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, the research involved collaboration with several institutions worldwide, highlighting the global effort to combat systemic sclerosis.
Systemic sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, affects approximately 2.5 million people globally. It is characterised by the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues, often resulting in severe complications. The disease’s complex genetic underpinnings have long posed challenges for researchers seeking to develop effective treatments.
Insights into Systemic Sclerosis
The study’s findings offer new insights into the genetic landscape of systemic sclerosis. By identifying previously unknown genetic contributors, researchers can better understand the disease’s pathogenesis. This knowledge is crucial for developing targeted therapies that can alleviate symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
Machine learning played a pivotal role in the study, allowing researchers to analyse extensive datasets and identify patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. “The power of machine learning lies in its ability to handle complex datasets and uncover hidden genetic patterns,” explained Dr. Sarah Johnson, a co-author of the study. “This technology is revolutionising the way we approach genetic research.”
The Potential Impact of the Findings
The identification of new genetic contributors to systemic sclerosis opens the door for personalised medicine approaches. By understanding the specific genetic variations that increase an individual’s risk, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to the patient’s unique genetic profile.
This personalised approach could significantly improve the quality of life for patients with systemic sclerosis. “Our findings represent a major step forward in the quest for personalised treatments,” said Dr. Smith. “By targeting the underlying genetic causes, we can develop therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects.”
Looking Ahead: The Future of Systemic Sclerosis Research
The study’s success underscores the importance of integrating new technologies, such as machine learning, into genetic research. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of systemic sclerosis, they remain optimistic about the potential for developing more effective treatments.
Continued collaboration between geneticists, rheumatologists, and data scientists will be crucial in advancing our understanding of systemic sclerosis. The research team’s innovative approach serves as a model for future studies, highlighting the potential of interdisciplinary collaboration in tackling complex diseases.
As the medical community absorbs these findings, the hope is that they will lead to new clinical trials and, ultimately, more effective treatments for systemic sclerosis. The study’s authors emphasise the importance of ongoing research and the need for continued investment in understanding autoimmune diseases.
By shedding light on the genetic factors that contribute to systemic sclerosis, this study marks a significant step forward in the fight against autoimmune diseases. The integration of exome sequencing and machine learning represents a promising avenue for future research, offering hope to millions of patients worldwide.






